Bloggfćrslur mánađarins, júlí 2024
27.7.2024 | 20:03
Hćtta á hjartavöđvabólgu margfaldađist eftir mRNA covid bólusetningu
Niđurstöđur óvenju umfangsmikillar ritrýndrar rannsóknar í Suđur Kóreu leiddu í ljós 620% aukna hćttu á hjartavöđvabólgu međal mRNA covid bólusettra og 175% aukna hćttu á gollurhússbólgu samanboriđ viđ söguleg viđmiđ. Heilsufarsupplýsingar 99% ţjóđarinnar lágu undir í rannsókninni hverra niđurstöđur voru birtar nýlega í Nature Communications. Fylgst var međ 4.5 milljónum bólusettra einstaklinga ađ međaltali í 15 mánuđi eftir bólusetningu. Ţar sem hátt bólusetningarhlutfall fullorđinna í Suđur Kóreu (96,6%) kom í veg fyrir samanburđ viđ nćgilega stórt úrtak óbólusettra voru söguleg gögn fyrir upphaf bólusetninga ţ.e. til 31.12.20 notuđ fyrir viđmiđunarhópinn og fylgst međ bólusetta hópnum til 31.12.22.
27.7.2024 | 10:32
Vísindagreinar um skađsemi covid bóluefnanna
Ljóst er af neđangreindri upptalningu vísindagreina, sem margar eru ritrýndar, ásamt greinum sem birst hafa í fagtímaritum um skađsemi covid bóluefnanna ađ ţúsundir vísindamanna taka ekki undir fullyrđingar um ađ bóluefnin til varnar Covid-19 flensunni séu bćđi örugg og gagnleg sem sýkinga- og smitvörn og hafa rökstutt ţađ viđhorf međ niđurstöđum rannsókna. Áhugasamir geta hér nálgast hlekki á greinarnar ásamt stuttri lýsingu á efni ţeirra. Greinarnar eru gróflega flokkađar eftir skađa af völdum bóluefnanna eftir sjúkdómum eđa skađa á einstök líffćri eđa líffćrakerfi. Hér er einungis listi yfir á annađ hundruđ rannsóknir en ţćr skipta orđiđ ţúsundum.
General Adverse Events
- Serious Adverse Events of Special Interest Following mRNA Vaccination in Randomized Trials
- Potential health risks of mRNA-based vaccine therapy: A hypothesis
- ‘Spikeopathy’: COVID-19 Spike Protein Is Pathogenic, from Both Virus and Vaccine mRNA
- The Novelty of mRNA Viral Vaccines and Potential Harms: A Scoping Review
- COVID-19 vaccines – An Australian Review
- National Academies Committee on Review of Relevant Literature Regarding Adverse Events Associated with Vaccines March 30 2023: Written material accompanying oral remarks
- Is the US’s Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System broken?
- Gene-based COVID-19 vaccines: Australian perspectives in a corporate and global context
- mRNA vaccine boosters and impaired immune system response in immune compromised individuals: a narrative review
- COVID-19 vaccines and adverse events of special interest: A multinational Global Vaccine Data Network (GVDN) cohort study of 99 million vaccinated individuals
- Exploring COVID-19 Vaccines ‘Safety Signal’ Data on Vigiaccess.org: A World Council for Health Report
- The mRNA-LNP vaccines – the good, the bad and the ugly?
- N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA causes +1 ribosomal frameshifting
- Broad-spectrum of non-serious adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination: A population-based cohort study in Seoul, South Korea
- Hematologic abnormalities after COVID-19 vaccination: A large Korean population-based cohort study
- BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccination in children alters cytokine responses to heterologous pathogens and Toll-like receptor agonists
- Concern about the Effectiveness of mRNA Vaccination Technology and Its Long-Term Safety: Potential Interference on miRNA Machinery
- Potential health risks of mRNA-based vaccine therapy: A hypothesis
- Detection of recombinant Spike protein in the blood of individuals vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2: Possible molecular mechanisms
- SARS-CoV-2 spike mRNA vaccine sequences circulate in blood up to 28 days after COVID-19 vaccination
- The spike hypothesis in vaccine-induced adverse effects: questions and answers
- Curing the pandemic of misinformation on COVID-19 mRNA vaccines through real evidence-based medicine - Part 1
- Shedding of infectious SARS-CoV-2 despite vaccination
- COVID-19 Vaccine Boosters for Young Adults: A Risk-Benefit Assessment and Five Ethical Arguments against Mandates at Universities
- Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs
- The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood–brain barrier in mice
- Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
- Previous COVID-19 infection but not Long-COVID is associated with increased adverse events following BNT162b2/Pfizer vaccination
- On COVID vaccines: why they cannot work, and irrefutable evidence of their causative role in deaths after vaccination
- Understanding the Pharmacology of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: Playing Dice with the Spike?
- Inability to work following COVID-19 vaccination–a relevant aspect for future booster vaccinations
- The anti-SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine suppresses mithramycin-induced erythroid differentiation and expression of embryo-fetal globin genes in human erythroleukemia K562 cells
- US COVID-19 Vaccines Proven to Cause More Harm than Good Based on Pivotal Clinical Trial Data Analyzed Using the Proper Scientific Endpoint, “All Cause Severe Morbidity”
- Brief research report: impact of vaccination on antibody responses and mortality from severe COVID-19
- Long-term adverse events of three COVID-19 vaccines as reported by vaccinated physicians and dentists, a study from Jordan and Saudi Arabia
Autoimmune
- Oncogenesis and autoimmunity as a result of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination
- The Potential Role of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccines in Multiple Sclerosis Onset and Reactivation: A Case Series and Literature Review
- Safety of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: results from the EULAR Coronavirus Vaccine (COVAX) physician-reported registry
- Autoimmune inflammatory reactions triggered by the COVID-19 genetic vaccines in terminally differentiated tissues
- Role of the antigen presentation process in the immunization mechanism of the genetic vaccines against COVID-19 and the need for biodistribution evaluations
- New-onset autoimmune phenomena post-COVID-19 vaccination
- IgA Vasculitis Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A French Multicenter Case Series Including 12 Patients
- Autoimmune inflammatory reactions triggered by the COVID-19 genetic vaccines in terminally differentiated tissues
- Molecular mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and mammalian proteomes: implications for the vaccine
- Incidence of Guillain-Barré Syndrome After COVID-19 Vaccination in the Vaccine Safety Datalink
- Pathogenic priming likely contributes to serious and critical illness and mortality in COVID-19 via autoimmunity
- Pathogenic antibodies induced by spike proteins of COVID-19 and SARS-CoV viruses
Blood Clots & Fibrous Clots
- COVID-19 Vaccines: A Risk Factor for Cerebral Thrombotic Syndromes
- Extensive splanchnic vein thrombosis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: A Vascular Liver Disease Group (VALDIG) initiative
- Sialylated Glycan Bindings from SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Blood and Endothelial Cells Govern the Severe Morbidities of COVID-19
- Safety Profiles of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines Using World Health Organization Global Scale Database (VigiBase): A Latent Class Analysis
- Adverse events following COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: A systematic review of cardiovascular complication, thrombosis, and thrombocytopenia
- Thrombosis Development After mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Administration: A Case Series
- Thromboembolic Events after COVID-19 Vaccination: An Italian Retrospective Real-World Safety Study
- Incidence and outcomes of splanchnic vein thrombosis after diagnosis of COVID-19 or COVID-19 vaccination: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Factors associated with stroke after COVID-19 vaccination: a statewide analysis
Cancer
- SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and the Multi-Hit Hypothesis of Oncogenesis
- Transfected SARS-CoV-2 spike DNA for mammalian cell expression inhibits p53 activation of p21(WAF1), TRAIL Death Receptor DR5 and MDM2 proteins in cancer cells and increases cancer cell viability after chemotherapy exposure
- Oncogenesis and autoimmunity as a result of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination
- Types and Rates of COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Microsatellite Stable and Instable Non-Metastatic Colon Cancer
- Review: N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ): Friend or foe of cancer?
- SARS-CoV-2 spike S2 subunit inhibits p53 activation of p21(WAF1), TRAIL Death Receptor DR5 and MDM2 proteins in cancer cells
- The impact of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine on adaptive and innate immune responses
- S2 subunit of SARS-nCoV-2 interacts with tumor suppressor protein p53 and BRCA: an in silico study
- The CD147 Epitope on SARS CoV2 and the Spike in Cancer, Autoimmunity and Organ Fibrosis
- Increased Age-Adjusted Cancer Mortality After the Third mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccine Dose During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Japan
Cardiac
- Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis
- OpenSAFELY: Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination in children and adolescents
- Improved diagnosis of COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis with cardiac scarring identified by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
- Forensic analysis of the 38 subject deaths in the 6-Month Interim Report of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine Clinical Trial
- Cardiac side effects of RNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: Hidden cardiotoxic effects of mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 on ventricular myocyte function and structure
- Duration of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine persistence and factors associated with cardiac involvement in recently vaccinated patients
- Assessment of Myocardial 18F-FDG Uptake at PET/CT in Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–vaccinated and Nonvaccinated Patients
- Cardiovascular Assessment up to One Year After COVID-19 Vaccine–Associated Myocarditis
- Sex-specific differences in myocardial injury incidence after COVID-19 mRNA-1273 booster vaccination
- Autopsy findings in cases of fatal COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis
- Cytokinopathy with aberrant cytotoxic lymphocytes and profibrotic myeloid response in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine–associated myocarditis
- Observed versus expected rates of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: a population-based cohort study
- Excess risk for acute myocardial infarction mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Catecholamines Are the Key Trigger of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine-Induced Myocarditis: A Compelling Hypothesis Supported by Epidemiological, Anatomopathological, Molecular, and Physiological Findings
- Clinical outcomes of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in four Nordic countries: population based cohort study
- Clinical cardiovascular emergencies and the cellular basis of COVID-19 vaccination: from dream to reality?
- SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and increased myocarditis mortality risk: A population based comparative study in Japan
- Myocarditis Cases Reported After mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination in the US From December 2020 to August 2021
- Changes of ECG [EKG] parameters after BNT162b2 vaccine in the senior high school students
- Myopericarditis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination Among Adolescents and Young Adults
- Circulating Spike Protein Detected in Post–COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Myocarditis
- Autopsy-based histopathological characterization of myocarditis after anti-SARS-CoV-2-vaccination
- Risks of myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmias associated with COVID-19 vaccination or SARS-CoV-2 infection
- BNT162b2 Vaccine-Associated Myo/Pericarditis in Adolescents: A Stratified Risk-Benefit Analysis
- Outcomes at least 90 days since onset of myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in adolescents and young adults in the USA: a follow-up surveillance study
- Increased emergency cardiovascular events among under-40 population in Israel during vaccine rollout and third COVID-19 wave
- Cardiovascular Manifestation of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Adolescents
- Age and sex-specific risks of myocarditis and pericarditis following Covid-19 messenger RNA vaccines
- Risk of Myopericarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in a Large Integrated Health System: A Comparison of Completeness and Timeliness of Two Methods
- Risk of Myocarditis After Sequential Doses of COVID-19 Vaccine and SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Age and Sex
- SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination-Associated Myocarditis in Children Ages 12-17: A Stratified National Database Analysis
- Epidemiology of Acute Myocarditis/Pericarditis in Hong Kong Adolescents Following Comirnaty Vaccination
- SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Myocarditis in a Nordic Cohort Study of 23 Million Residents
- Myocarditis Following COVID-19 BNT162b2 Vaccination Among Adolescents in Hong Kong
- Myocarditis and Pericarditis After Vaccination for COVID-19
- Abstract 10712: Observational Findings of PULS Cardiac Test Findings for Inflammatory Markers in Patients Receiving mRNA Vaccines
- The Incidence of Myocarditis and Pericarditis in Post COVID-19 Unvaccinated Patients-A Large Population-Based Study
- COVID-19-Associated cardiac pathology at the postmortem evaluation: a collaborative systematic review
- Adjuvants in COVID-19 vaccines: innocent bystanders or culpable abettors for stirring up COVID-heart syndrome
- Arrhythmias after COVID-19 Vaccination: Have We Left All Stones Unturned?
- Risks of Cardiac Arrhythmia Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dermatological
- New Onset and Exacerbations of Psoriasis Following COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review
- Management of oral lesions following COVID-19 vaccination
- Occurrence of erythema multiforme following COVID-19 vaccination: a review
- Incidence of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Following Receipt of the COVID-19 Vaccine Booster in Switzerland
- A systematic review on mucocutaneous presentations after COVID-19 vaccination and expert recommendations about vaccination of important immune-mediated dermatologic disorders
- Cutaneous vasculitis: Lessons from COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination
Diabetes
- Metformin mitigates insulin signaling variations induced by COVID-19 vaccine boosters in type 2 diabetes
- Hyperglycemic Emergencies Associated With COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Series and Discussion
Eye Disorders
- Characteristics and Clinical Ocular Manifestations in Patients with Acute Corneal Graft Rejection after Receiving the COVID-19 Vaccine: A Systematic Review
- Risk assessment of retinal vascular occlusion after COVID-19 vaccination
- COVID-19 Vaccine-Associated Optic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review of 45 Patients
- The Eye of the Storm: COVID-19 Vaccination and the Eye
- Ocular Complications Following Vaccination for COVID-19: A One-Year Retrospective
- UVEITIS AFTER THE BNT162b2 mRNA VACCINATION AGAINST SARS-CoV-2 INFECTION: A Possible Association
- Retinal Toxicity of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-400
Increased Susceptibility to C19 Infection
- Risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization in individuals with natural, vaccine-induced and hybrid immunity: a retrospective population-based cohort study from Estonia
- IgG4 Antibodies Induced by Repeated Vaccination May Generate Immune Tolerance to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
- Forgotten “Primum Non Nocere” and Increased Mortality after COVID-19 Vaccination
- Effectiveness of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Bivalent Vaccine (Known as the Cleveland Clinic study
- Antinucleocapsid Antibodies After SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Blinded Phase of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Clinical Trial
- Effectiveness of mRNA-1273 vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.2, BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5
- Class switch toward noninflammatory, spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after repeated SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
- Conserved longitudinal alterations of anti-S-protein IgG subclasses in disease progression in initial ancestral Wuhan and vaccine breakthrough Delta infections
- Duration of Shedding of Culturable Virus in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (BA.1) Infection
- Immune boosting by B.1.1.529 (Omicron) depends on previous SARS-CoV-2 exposure
- Increases in COVID-19 are unrelated to levels of vaccination across 68 countries and 2947 counties in the United States
- Informed consent disclosure to vaccine trial subjects of risk of COVID-19 vaccines worsening clinical disease
- Effects of Vaccination and Previous Infection on Omicron Infections in Children
- (SARS-CoV-2) Naturally Acquired Immunity versus Vaccine-induced Immunity, Reinfections versus Breakthrough Infections: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfections as Compared with Primary Infections
- Elevated risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2 Beta, Gamma, and Delta variant compared to Alpha variant in vaccinated individuals
Inflammation
- Correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders
- New-Onset Rheumatic Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinations until May 2023: A Systematic Review
- Abstract 10712: Observational Findings of PULS Cardiac Test Findings for Inflammatory Markers in Patients Receiving mRNA Vaccines
- Reported cases of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children aged 12–20 years in the USA who received a COVID-19 vaccine, December, 2020, through August, 2021: a surveillance investigatio
- SARS-CoV-2 vaccination can elicit a CD8 T-cell dominant hepatitis
- Cutaneous vasculitis: Lessons from COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination
- Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: A registry-based study of 414 cases
Kidney / Renal Issues
- Renal Complications Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Narrative Literature Review
- Daily Clout Report 62: Acute Kidney Injury and Acute Renal Failure Following Pfizer mRNA COVID Vaccination
- Case Report: Anti-neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis With Acute Renal Failure and Pulmonary Hemorrhage May Occur After COVID-19 Vaccination
- Successful treatment of new-onset diabetes mellitus and IgA nephropathy after COVID-19 vaccination: a case report
- Minimal Change Disease After First Dose of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine: A Case Report and Review of Minimal Change Disease Related to COVID-19 Vaccine
Long COVID versus Long Vax
- Long COVID: Sufferers can take heart
- Persistence of S1 Spike Protein in CD16+ Monocytes up to 245 Days in SARS-CoV-2 Negative Post COVID-19 Vaccination Individuals with Post-Acute Sequalae of COVID-19 (PASC)-Like Symptoms
- Presence of viral spike protein and vaccinal spike protein in the blood serum of patients with long-COVID syndrome
- Characteristics and predictors of Long COVID among diagnosed cases of COVID-19
- The prevalence of post-COVID-19 vaccination syndrome and quality of life among COVID-19-vaccinated individuals
- Post-Vaccination Syndrome: A Descriptive Analysis of Reported Symptoms and Patient Experiences After Covid-19 Immunization
- Association between virus variants, vaccination, previous infections, and post-COVID-19 [“Long Covid”] risk
- Persistent Circulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Is Associated With Post-acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sequelae
- Strategies for the Management of Spike Protein-Related Pathology
- Persistent circulation of soluble and extracellular vesicle-linked Spike protein in individuals with postacute sequelae of COVID-19
- Long-COVID Prevalence and Its Association with Health Outcomes in the Post-Vaccine and Antiviral-Availability Era
Neurological Issues
- Prenatal Exposure to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine BNT162b2 Induces Autism-Like Behaviors in Male Neonatal Rats
- Emergence of a New Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease: 26 Cases of the Human Version of Mad-Cow Disease, Days After a COVID-19 Injection
- COVID-19 vaccination-related tinnitus is associated with pre-vaccination metabolic disorders
- Audiovestibular adverse events following COVID-19 vaccinations
- Vestibular Neuritis Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Retrospective Study
- Vertigo/dizziness following COVID-19 vaccination
- Preliminary Evidence of a Link between COVID-19 Vaccines and Otologic Symptoms
- NEURO-COVAX: An Italian Population-Based Study of Neurological Complications after COVID-19 Vaccinations
- Neurological Adverse Reactions to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
- SARS-CoV-2 Spike amyloid fibrils specifically and selectively accelerates amyloid fibril formation of human prion protein and the amyloid β peptide
- Apparent risks of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome diagnoses after COVID-19 vaccination and SARS-Cov-2 Infection
- SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Accumulation in the Skull-Meninges- Brain Axis: Potential Implications for Long-Term Neurological Complications in post-COVID-19
- CUMULATIVE ANALYSIS OF POST-AUTHORIZATION ADVERSE EVENT REPORTS OF PF-07302048 (BNT162B2) RECEIVED THROUGH 28-FEB-2021
- A Potential Role of the Spike Protein in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Narrative Review
- Reports of Guillain-Barré Syndrome After COVID-19 Vaccination in the United States
- Neurological Complications Following COVID‐19 Vaccination
- Sudden Hearing Loss Following Vaccination Against COVID-19
- Development of facial palsy following COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review
- COVID-19 RNA Based Vaccines and the Risk of Prion Disease
- SARS-CoV-2 S1 Protein Induces Endolysosome Dysfunction and Neuritic Dystrophy
- Neurological consequences of COVID-19 and brain related pathogenic mechanisms: A new challenge for neuroscience
- Immediate and 6-month seizure outcomes following first and second SARS-CoV2 mRNA vaccinations: A multicenter study with a nationwide survey
- Factors associated with stroke after COVID-19 vaccination: a statewide analysis
Reactivation of Latent Viruses
- Association of herpes zoster with COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Reproductive Issues
- Transplacental transmission of the COVID-19 vaccine messenger RNA: evidence from placental, maternal, and cord blood analyses postvaccination
- Increased risk of fetal loss after COVID-19 vaccination
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Among COVID-19 Vaccinated and Recovered Women: a National Survey
- A Nationwide Survey of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccinee’s Experiences on Adverse Events and Its Associated Factors
- Evaluation of menstrual symptoms after Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in women with endometriosis
- Female reproduction and abnormal uterine bleeding after COVID-19 vaccination
- Heavy bleeding and other menstrual disturbances in young women after COVID-19 vaccination
- Prevalence of and risk factors for self-reported menstrual changes following COVID-19 vaccination: a Danish cohort study
- Association between Different Types of COVID-19 Vaccines and Menstrual Cycle Patterns among Women of Reproductive Age
- Unexpected vaginal bleeding and COVID-19 vaccination in non-menstruating women
- Biodistribution of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in human breast milk
- Premenstrual and menstrual changes reported after COVID-19 vaccination: The EVA project
- Safety of third SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (booster dose) during pregnancy
- Analysis of Vaccine Reactions After COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Doses Among Pregnant and Lactating Individuals
- COVID-19 Vaccines: The Impact on Pregnancy Outcomes and Menstrual Function
- Japanese Pfizer biodistribution studies translated: SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine (BNT162, PF-07302048) 2.6.4 Summary statement of the pharmacokinetic study
- Detection of Messenger RNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Human Breast Milk
- Menstrual cycle disturbances after COVID-19 vaccination
- The effect of BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine on menstrual cycle symptoms in healthy women
- Covid-19 vaccination BNT162b2 temporarily impairs semen concentration and total motile count among semen donors
- Neutralizing Activity and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine mRNA Persistence in Serum and Breastmilk After BNT162b2 Vaccination in Lactating Women
Reverse Transcription of the Genome
- Methodological Considerations Regarding the Quantification of DNA Impurities in the COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Comirnaty®
- Presence of viral spike protein and vaccinal spike protein in the blood serum of patients with long-COVID syndrome
- DNA fragments detected in monovalent and bivalent Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna modRNA COVID-19 vaccines from Ontario, Canada: Exploratory dose response relationship with serious adverse events
- Sequencing of bivalent Moderna and Pfizer mRNA vaccines reveals nanogram to microgram quantities of expression vector dsDNA per dose
- SARS-CoV-2 RNA reverse-transcribed and integrated into the human genome
- Intracellular Reverse Transcription of Pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine BNT162b2 In Vitro in Human Liver Cell Line
- mRNA: Vaccine or Gene Therapy? The Safety Regulatory Issues
Thyroid Dysfunction
- Effect of SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine on thyroid autoimmunity: A twelve-month follow-up study
Vaccine Shedding
- Inadvertent Exposure to Pharmacologically Designed Lipid Nanoparticles Via Bodily Fluids: Biologic Plausibility and Potential Consequences
- SHEDDING OF COVID mRNA VACCINES: A review of the available evidence
- Current state of knowledge on the excretion of mRNA and spike produced by anti-COVID-19 mRNA vaccines; possibility of contamination of the entourage of those vaccinated by these products
Excess Deaths & SADS
- Spatiotemporal variation of excess all-cause mortality in the world (125 countries) during the Covid period 2020-2023 regarding socio economic factors and public-health and medical interventions
- COVID-19 Illness and Vaccination Experiences in Social Circles Affect COVID-19 Vaccination Decisions
- COVID-19 vaccine-associated mortality in the Southern Hemisphere
- A Systematic REVIEW of Autopsy findings in deaths after covid-19 vaccination
- Is There a Link between the 2021 COVID-19 Vaccination Uptake in Europe and 2022 Excess All-Cause Mortality?
- Deaths by vaccination status, England
- Excess mortality in Germany 2020-2022
- Postmortem investigation of fatalities following vaccination with COVID-19 vaccines
- Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immune Response and Sudden Death: Titin as a Link
- Risk of COVID Vaccine-Induced Fatality is Equal to or Greater than the Risk of a COVID death for all Age Groups Under 80 Years Old
- Covid-19: Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is “likely” responsible for deaths of some elderly patients, Norwegian review finds
- US - Trends in Death Rates from Neoplasms, Ages 15-44
Other Articles Compiling Studies on Vaccine Injury
25.7.2024 | 18:19
Međalćvin styttist tvö ár í röđ
Ólifuđ međalćvi karla viđ fćđingu hefur styst um 0,7 ár og kvenna um 0,6 ár frá 2021. Međalćvi landsmanna hefur međ örfáum undatekningum lengst á hverju ári síđustu áratugi en eftir styttingu síđustu tveggja ára er međalćvin nú orđin svipuđ og hún var fyrir 10 til 12 árum.
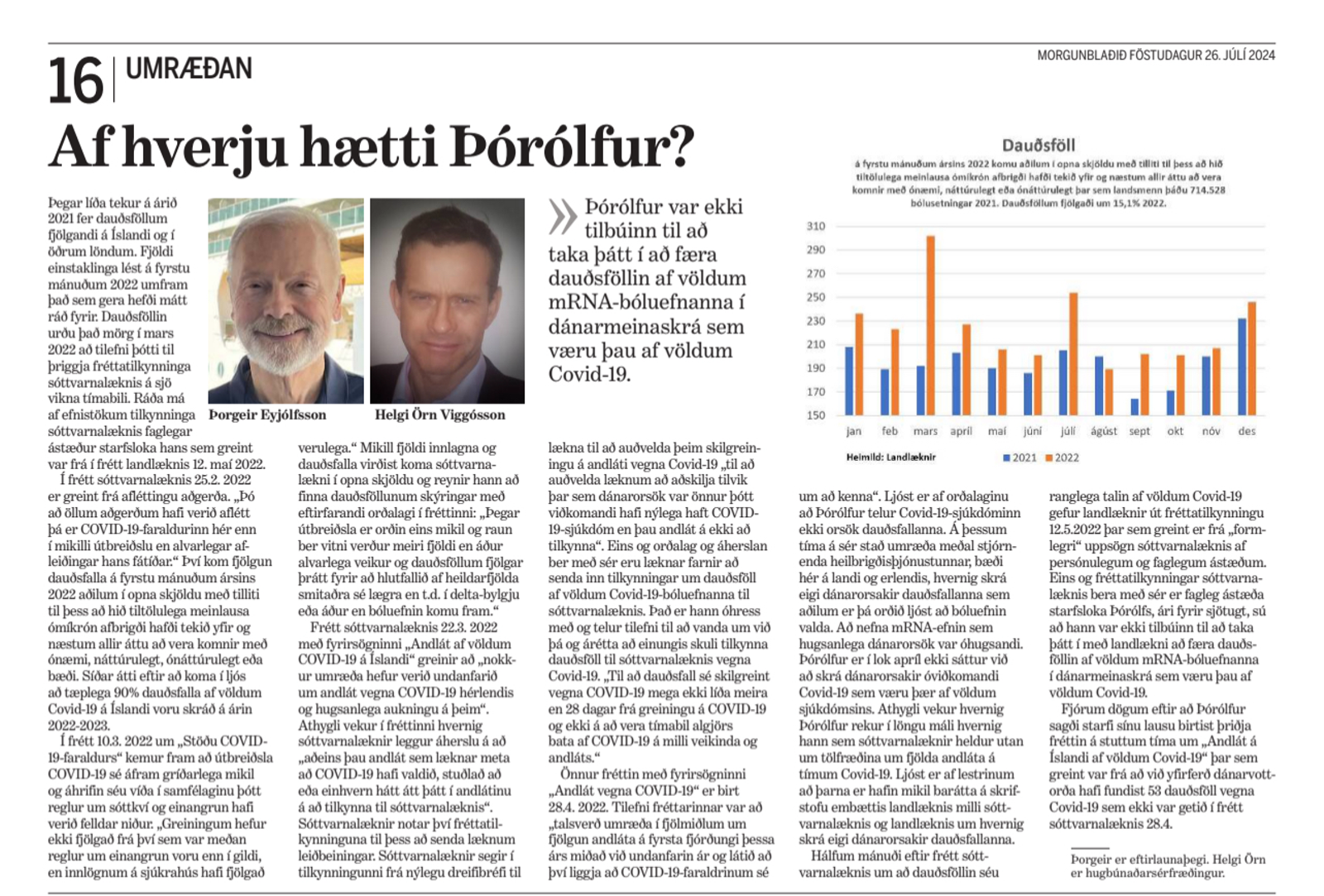
Lokaorđ eftirminnilegs svars Guđrúnar Aspelund sóttvarnalćknis, ţar sem lćknirinn var spurđur álits á niđurstöđum ítalskrar rannsóknar í milljóna hérađi á Ítalíu sem sýndu augljósa fylgni milli mRNA bólusetninganna gegn covid og fjölgunar dauđsfalla sem fylgdu, voru ţau ađ „ţađ er algjörlega búiđ ađ sýna fram á ţađ ađ Covid-19 bóluefnin eru gagnleg og ávinningur langt umfram áhćttu.“ Ađ ţeim stóradómi föllnum er ekki nema von ađ menn spyrji hvernig á ţví standi ađ međalćvi Íslendinga hafi tekiđ ađ styttast fyrir tveimur árum eftir ađ landsmenn höfđu ţegiđ yfir 700.000 bóluefnaskammta gegn covid međ „namminu“ hans Kára Stefánssonar? Hvernig standi á ţví ađ dánartíđni ungbarna hćkki um 64% á árinu 2023 hvort sem miđađ er viđ fyrra ár eđa međaltal áranna 2018/2019?
Ađ ţeim stóradómi föllnum er ekki nema von ađ menn spyrji hvernig á ţví standi ađ međalćvi Íslendinga hafi tekiđ ađ styttast fyrir tveimur árum eftir ađ landsmenn höfđu ţegiđ yfir 700.000 bóluefnaskammta gegn covid međ „namminu“ hans Kára Stefánssonar? Hvernig standi á ţví ađ dánartíđni ungbarna hćkki um 64% á árinu 2023 hvort sem miđađ er viđ fyrra ár eđa međaltal áranna 2018/2019?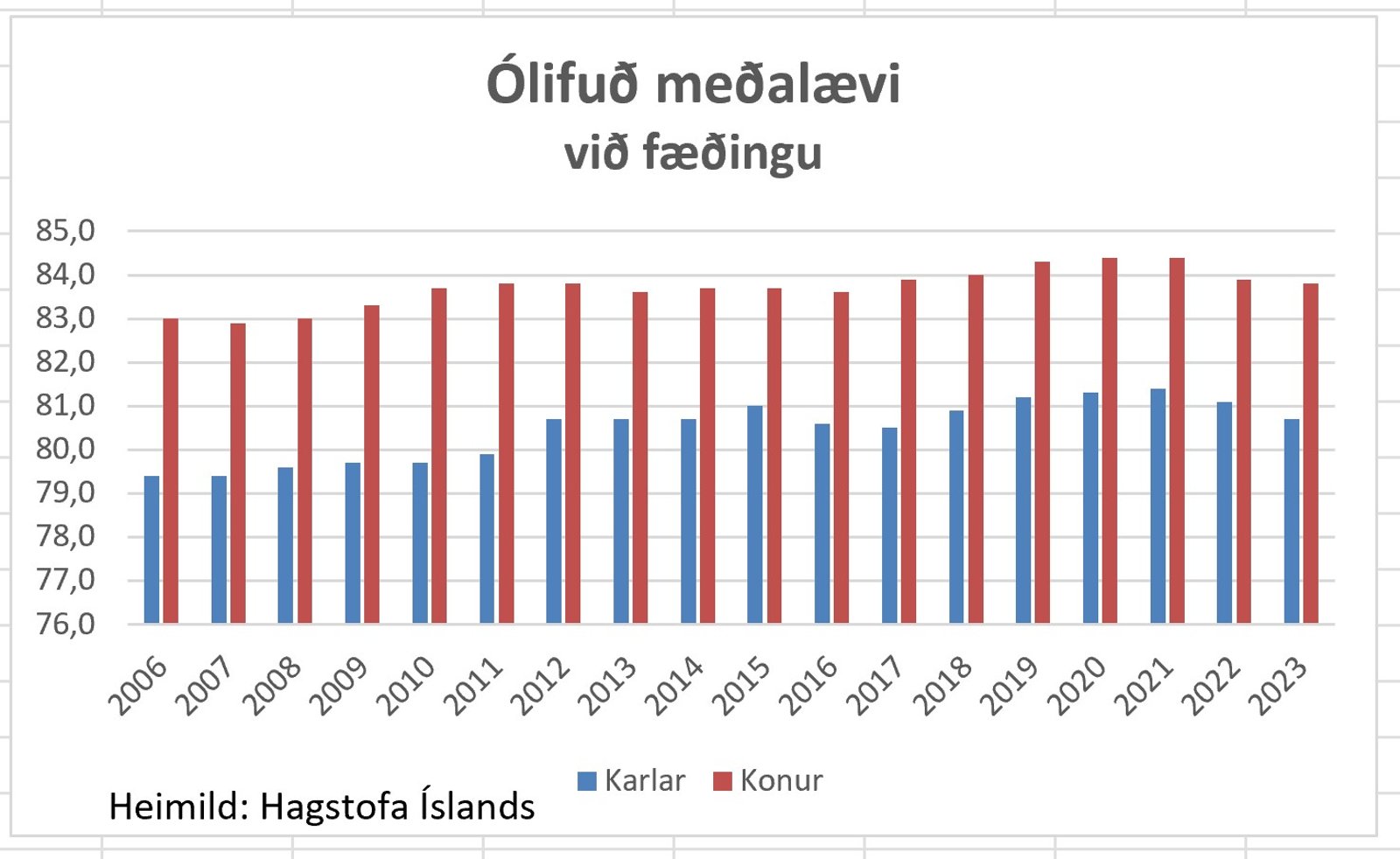
25.7.2024 | 12:34
Dánartíđni ungbarna hćkkar um 64% og nýbura um 47% milli ára
Hagstofa Íslands hefur náđ ađ taka saman tölur um fćđingar og andlát á árinu 2023. Dánartíđni nýbura (ţ.e. barna sem látast innan 28 daga frá fćđingu) hćkkar um 47% á milli ára og dánartíđni ungbarna (ţ.e. barna sem látast á fyrsta aldursári) hćkkar um 64% reiknađ af 1.000 lifandi fćddum börnum. Sé dánartíđni barnanna reiknuđ miđuđ viđ međaltal áranna 2018 og 2019 kemur í ljós ađ dánartíđni nýbura hefur hćkkađ um 56% og ungbarna um 64% pr. 1.000 lifandi fćđingar.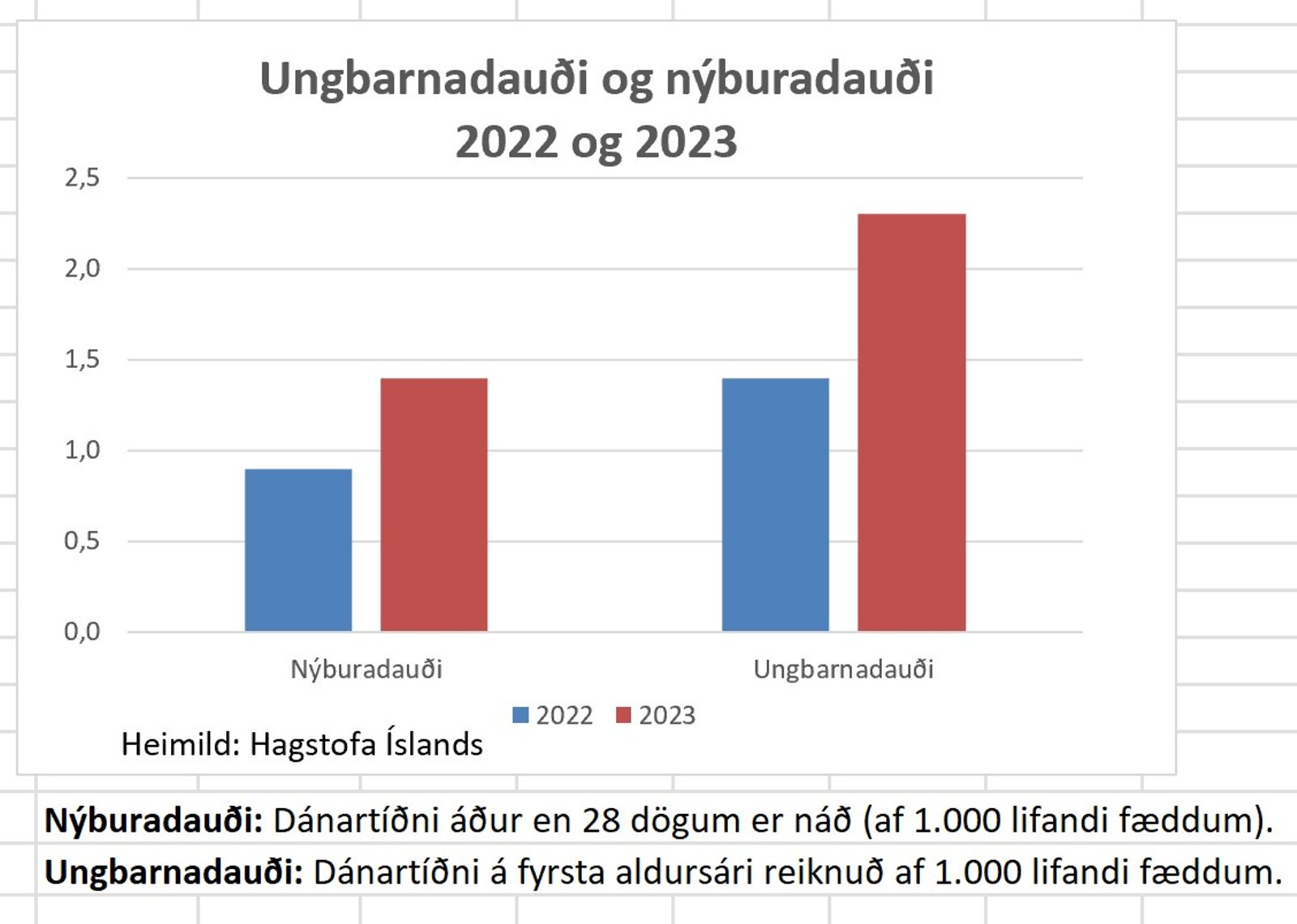
24.7.2024 | 15:33
Frasinn súrnar
Fyrir ţau sem ekki hafa tíma aflögu til ađ kynna sér niđurstöđur rannsókna sem benda sterklega til orsakasambands Covid mRNA bólusetninganna og fjölgunar dauđsfalla í kjölfariđ kann međfylgjandi súlurit úr ástralskri skýrslu ađ vera hjálplegt. Súluritiđ sýnir fjölgun tilkynninga inn í gagnagrunn um bóluefnaskađa í Vestur Ástralíu viđ upphaf bólusetninga međ mRNA covid efnunum sem hófust í mars 2021. Ekki er hćgt ađ skýra fjölgun tilkynninga um bóluefnaskađa međ Covid-19 flensunni ţví enginn hafđi á ţeim tíma greinst međ veiruna vegna einangrunar fylkisins ţar sem algert ferđabann ríkti. Ţađ var ekki fyrr en síđar á árinu ađ covid flensunnar varđ vart. Tekiđ var til ţess á blađamannafundi forsćtisráđherrans í október 2021 hvernig hann kunni engar skýringar á yfirfullum spítölum. Enginn var jú međ covid.
Frasinn um ađ fylgni sé ekki sama og orsök á ekki lengur viđ ţegar fjallađ er um mRNA efnin og umframdauđsföllin. Svo margar eru rannsóknirnar orđnar hverra niđurstöđur leiđa sterkar líkur ađ orsakasambandi.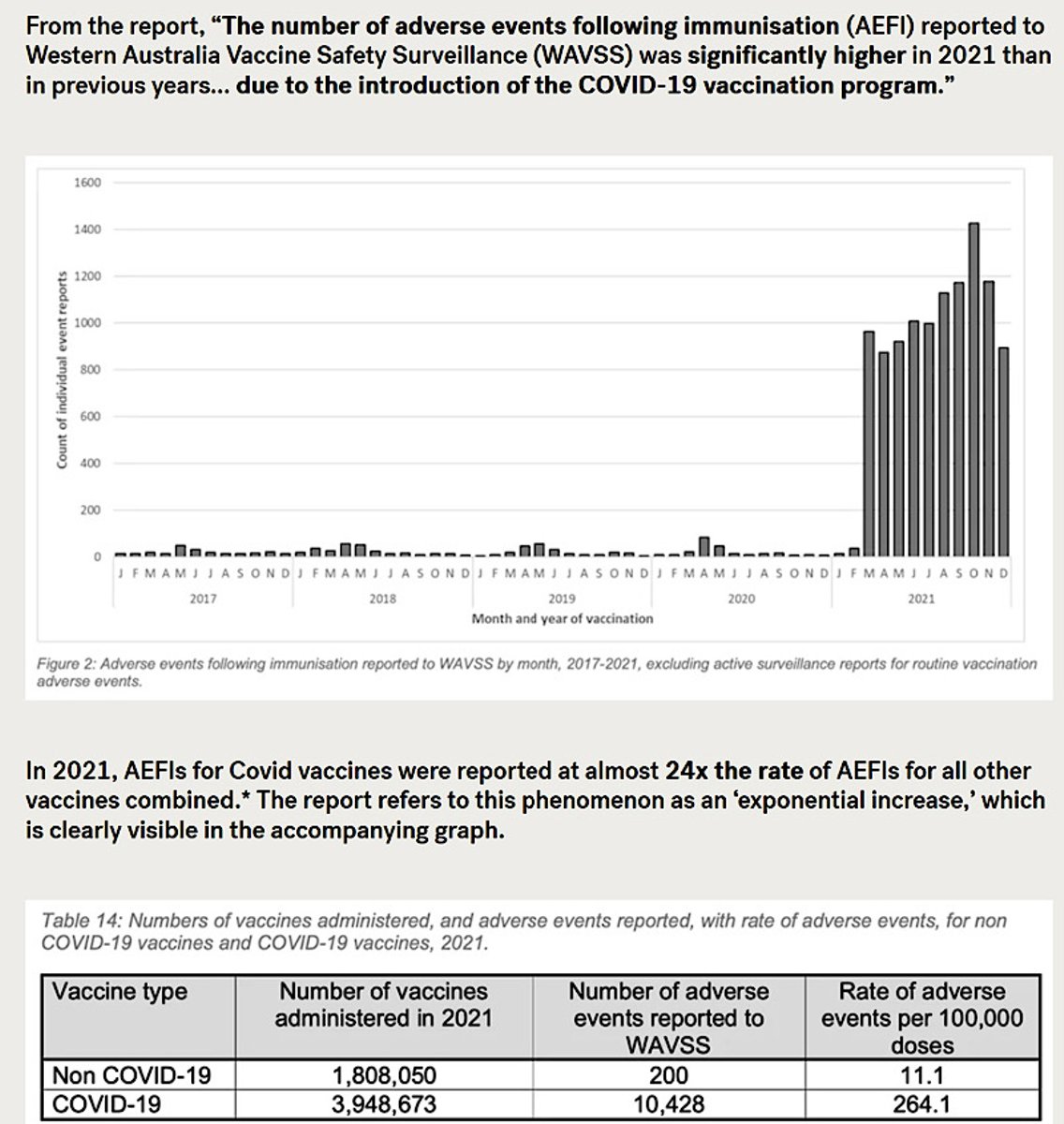
23.7.2024 | 21:30
Var sama fljótaskriftin međ barnabóluefnin?
Fćstir foreldrar hafa tíma aflögu í brauđstriti dagsins til ađ kynna sér bóluefnin sem notuđ eru viđ barnabólusetningar hér á landi. Ţađ kemur ţvi mörgum á óvart ţegar ţeir uppgötva ađ engin bóluefnanna sem Sóttvarnastofnun Bandaríkjanna (CDC) hefur samţykkt til notkunar hefur veriđ reynt í langtíma klínískum tvíblindum rannsóknum. Ţađ er rannsókn ţar sem hluta barnanna er gefin lyfleysa (saltlausn) og hvorki ţátttakendur eđa umsjónarmenn rannsóknarinnar vita hvort barn var sprautađ međ virka efninu eđa lyfleysunni. Til ađ auđvelda foreldrum ađ glöggva sig á bóluefnunum er í klippunni listi yfir efnin međ upplýsingum um tímalengd rannsókna. Í hlekknum má nálgast ítarlegri upplýsingar um efnin og hlekki á fylgiseđla ţeirra ásamt stuttri lýsingu á prófunum.
Foreldrum um heim allan fjölgar (ţátttaka i barnabólusetningum dregst saman) sem spyrja hvers vegna ţau ćttu ađ geta treyst heilbrigđisyfirvöldum til ađ hafa heilbrigđi barnanna í fyrirrúmi međan ennţá er haldiđ áfram ađ nota mRNA efnin ţrátt fyrir ađ flestir hafi fyrir augum eđa ţekki til alvarlegs skađa sem efnin hafa valdiđ.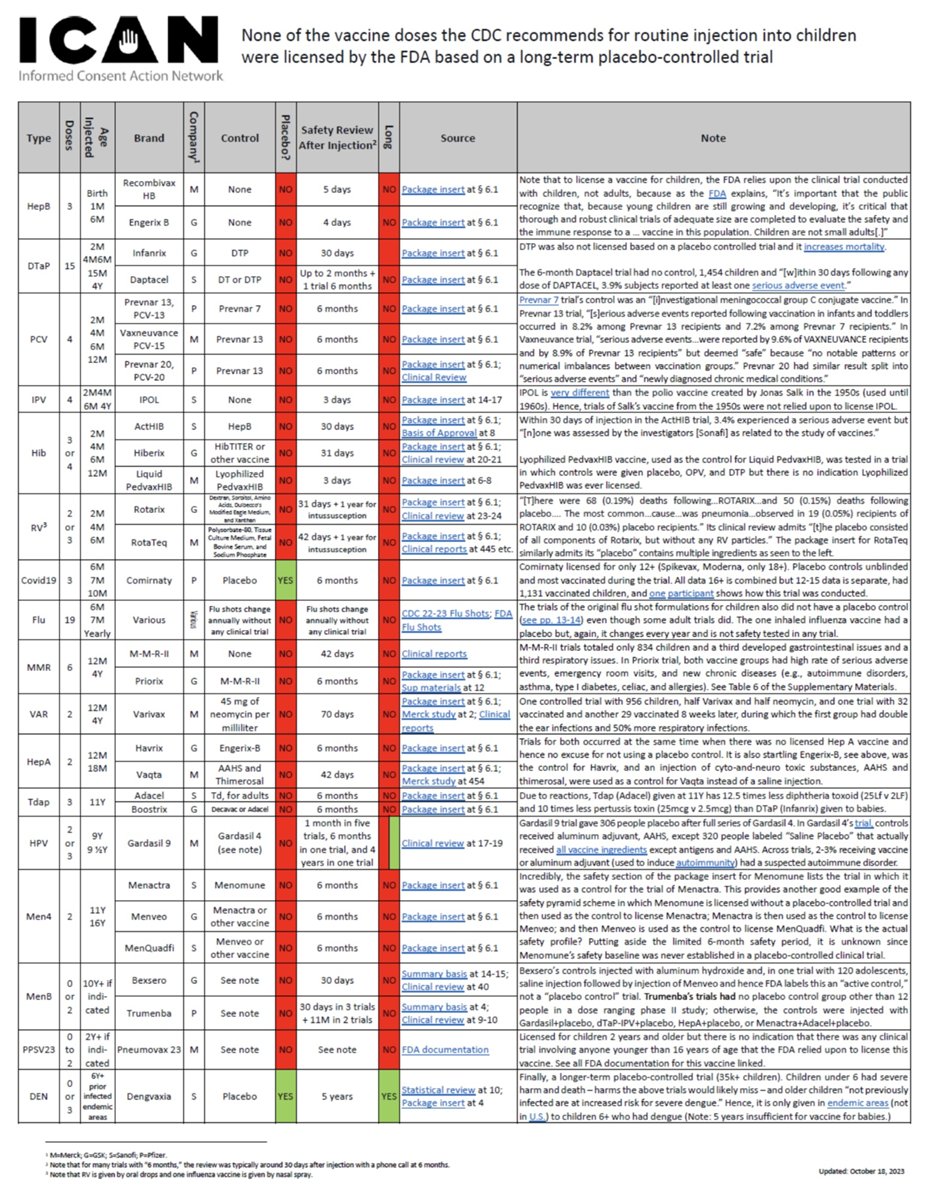
22.7.2024 | 10:27
Orsakasambandiđ geirneglt af ţýskri nákvćmni
Ţađ er ađ bera í bakkafullan lćkinn ađ kynna til sögunnar enn eina rannsóknina sem leiđir sterkar líkur ađ orsakasambandi covid bólusetninganna og fjölgunar dauđsfalla. Niđurstöđur ţýskrar rannsóknar, sem enn hefur ekki gefist tóm til ađ ritrýna, á áhrifum Covid-19 á dauđsföll í 16 sambandsríkjum yfir ţriggja ára tímabil bćtist í ört stćkkandi hóp rannsókna sem leiđa sterkar líkur ađ orsakasambandi Covid bólusetninganna og fjölgunar dauđsfalla. Mantran um ađ fylgni sé ekki sama og orsök á ekki lengur viđ ţegar fjallađ er um mRNA efnin og umframdauđsföllin. Svo margar eru rannsóknirnar orđnar hverra niđurstöđur leiđa sterkar líkur ađ orsakasambandi.
21.7.2024 | 16:56
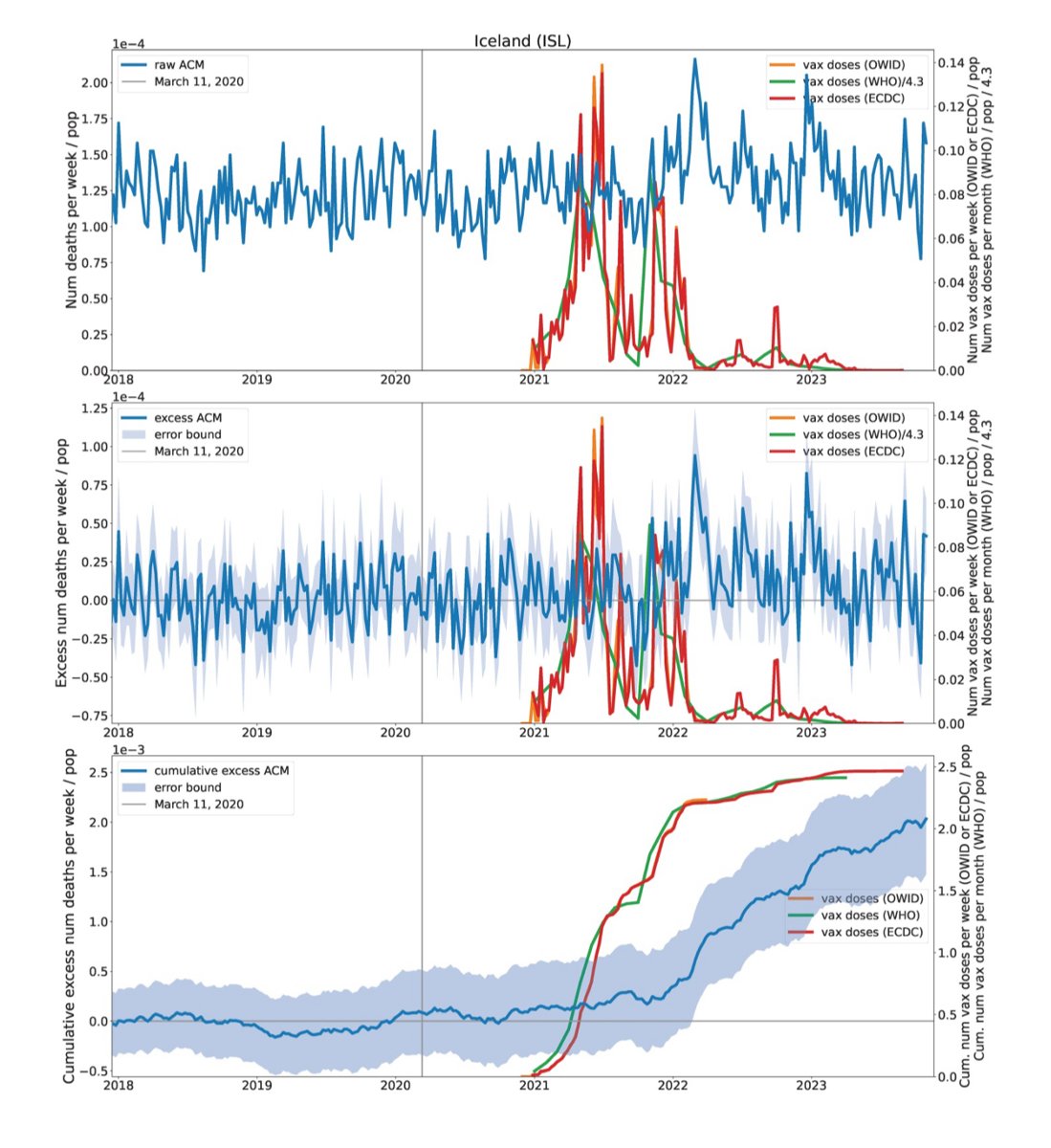
Ísland skólabókardćmi á heimsvísu um líklegt orsakasamband
Ísland er á međal 110 landa af 125 löndum í nýrri rannsókn ţar sem ítarleg gögn um bólusetningar ásamt upplýsingum um dauđsföll voru fyrirliggjandi og ađgengileg rannsóknarađilum. Í löndunum 110 (án undantekninga) var fylgnin milli bólusetninga og fjölgun dauđsfalla augljós. Klippan sýnir fylgni bólusetninga og dauđsfalla á Íslandi og er landiđ í hópi ţjóđa ţar sem fjölgun dauđsfalla í kjölfar örvunarbólusetninga seinni part árs 2021 er greinileg en dauđsföllum fjölgađi mikiđ hérlendis og náđu ţau hámarki í mars 2022. Ísland hefur um margra mánađa skeiđ veriđ í hópi ţeirra ţjóđa Evrópu sem flest hafa umframdauđsföllin.
Niđurstöđur óvenju stórrar rannsóknarinnar greina áhrif misráđinna sóttvarnaviđbragđa stjórnvalda víđa um heim og hvernig ţau leiddu til fjölgunar dauđsfalla. Hvergi í heiminum fćkkađi dauđsföllum í kjölfar bólusetninga gegn Covid og telja rannsakendur auđsćtt ađ fullyrđing ţess efnis ađ bóluefnin hafi bjargađ milljónum mannslífa eigi ekki viđ rök ađ styđjast.